


Unlike some other creatures that bite, leeches don’t cause stinging, carry diseases or leave a poisonous stinger in the wound. Leech bites are not dangerous or painful, just annoying. Even those that do drink blood aren’t actively looking for human blood-they prefer frogs, snails, turtles, and other aquatic creatures. Not all leeches suck blood Many freshwater leeches, in fact, don’t eat blood at all-they’re carnivores, but they stick to molluscs, insect larvae, and worms. A person could bleed to death if they sustained a massive number of leech bites, or die from a blood infection, Joslin says. In very rare cases, though, leech bites can be lethal. You probably won’t need to take antibiotics to prevent an infection, Joslin says.
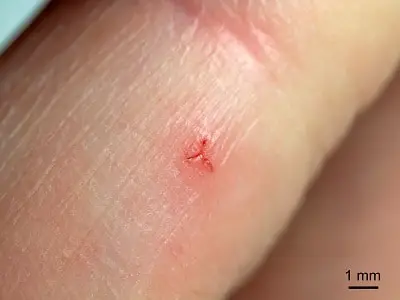
Then wash the area with soap and water and bandage it. Leeches are blood-feeding organisms that have a suite of anticoagulant compounds they secrete from their salivary glands that prevent blood clotting. Leech saliva contains hirudin, an anticoagulant and anti-platelet agent that works to prevent blood clots and reduce the amount of congested blood in the tissues. It increases the amount of blood sucked by a leech. It causes vasodilation of the blood vessels. Histamine-like substance is another protein that is found in the salivary cells of leeches. It is thought that the prolongation of bleeding after leech bite is mainly due to hirudin. 8 What causes a blood clot to form in a leech?.7 What happens if you get bitten by a leech?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
